Definition
A storage system is an architectural structure that manages drives and how to access them from the client OS.
There are three main types of storage systems:
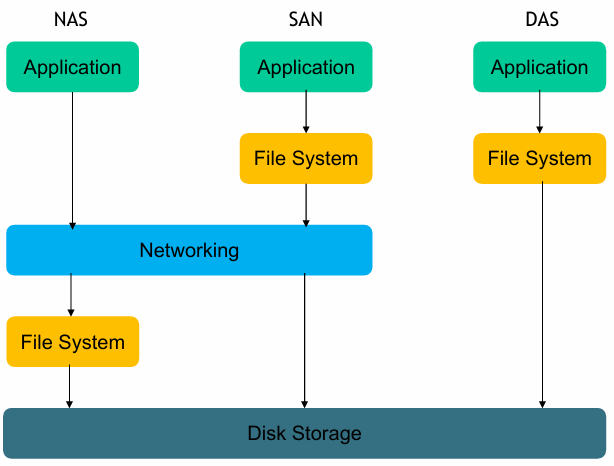
- Direct-attached storage (DAS): a storage system directly attached to a server or workstation. They are visible as disks/volumes by the client OS
- Network-attached storage (NAS): a computer connected to a network that provides only file-based data storage services (e.g., FTP, Network File System and SAMBA) to other devices on the network and is visible as File Server to the client OS
- Storage Area Networks (SAN): remote storage units that are connected to PC using a specific networking technology (e.g., Fiber Channel) and are visible as disks/volumes by the client OS
Direct-attached storage (DAS)
Definition
Direct-attached storage (DAS) is a storage system directly attached to a server or workstation, where disks are visible as disks/volumes by the client OS.
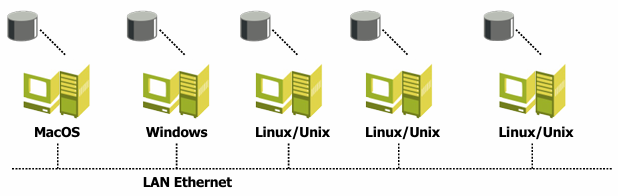
This type of storage system is the simplest one and is used in small environments where scalability (very limited) and management (complex) are not a priority. However, the performance are pretty limited and to read the files in other machines, there must be a sharing protocol (e.g., NFS, SMB, FTP) enabled that the OS can use to access the files.
DAS does not necessary mean “internal storage” because even a system where all the external disks are connected with a poit-to-point protocol to a PC can be considered as DAS. DAS is the most common storage system in the consumer market, where the user can connect an external hard disk to the PC using USB, Thunderbolt, or FireWire. In the enterprise market, DAS is used to extend the storage of a server, by connecting an external storage device to the server using a specific protocol (e.g., SCSI, SAS, SATA).
Network-attached storage (NAS)
Definition
Network-attached storage (NAS) is a computer connected to a network that provides only file-based data storage services to other devices on the network.
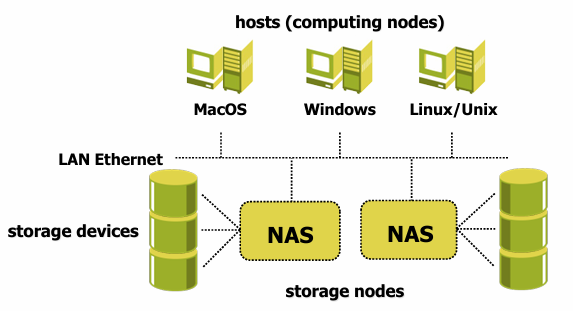
A NAS system can contain one or more hard disks, often organized into logical redundant storage containers or RAID arrays. NAS uses file-based protocols such as NFS (Network File System) or SMB/CIFS (Server Message Block/Common Internet File System) to provide shared access to files across the TCP/IP network.
Each NAS element has its own IP address and can be accessed by the client OS as a File Server using the file sharing protocol. The NAS system can be used to store files, to share files, to backup files, and to provide a storage solution for virtualization environments. The NAS system is a good solution for small and medium environments providing a good level of scalability, by adding more NAS devices to the network, and a good level of performance, by using a dedicated network for the NAS devices.
The key differences between DAS and NAS are that DAS is simply an extension of an existing server and is not necessary networked, while NAS is designed as an easy and self-contained solution for sharing files over the network. Comparing NAS with local DAS, the performance of NAS is limited by the network speed and the number of clients that can access the NAS at the same time.
Storage Area Networks (SAN)
Definition
Storage Area Networks (SAN) are remote storage units that are connected Servers using a specific networking technology.
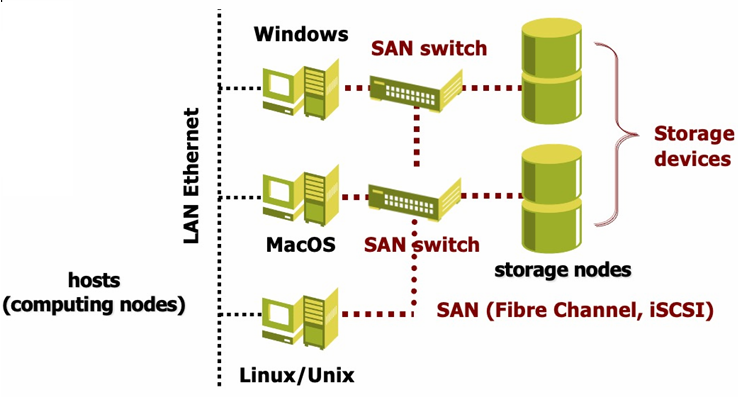
SANs have a special network devoted to access to storage devices, one TCP/IP network for the clients and another network for the storage devices based on fiber channel. This solution provides high scalability, by increasing the storage devices connected to the SAN, and high performance, by using a dedicated network for the storage devices.
While NAS provides both storage and file system, SAN provides only block-based storage and leaves file system concerns on the client side. NAS appears to the client OS as a file server (the client can map network drives to shares on that server), while a disk available through a SAN still appears to the client OS as a disk, visible in the disks and volumes management utils and available to be formatted with a file system.
Traditionally, NAS is used to low-volume access to a large amount of storage by many users, while SAN is the solution for petabyte of storage and multiple, simultaneous access to files. SAN is the best solution for virtualization environments, where the storage devices are shared between multiple servers, and for DBMS, where the performance of the storage devices is critical.
Comparison
| Application domain | Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DAS | - budget constraints - simple storage solutions | - easy setup - low cost - high performance | - limited accessibility - limited scalability - no central management and backup |
| NAS | - file storage and sharing - big data storage | - scalability - greater accessibility - performance | - increased LAN traffic - performance limitations - security and reliability |
| SAN | - DBMS - virtualization | - improved performance - greater scalability - high availability | - high cost - complex setup - high maintenance |